GranuFlo and NaturaLyte
GranuFlo and NaturaLyte are two substances manufactured and marketed by Fresenius Medical Care for use in dialysis treatments for acute and chronic kidney failure. Both concentrates have been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks and other health complications, sometimes resulting in death.
- Medically reviewed by Kenneth S. Fill, Pharm.D., MBA
- Last update: June 12, 2025
People undergoing dialysis may receive a solution to replace fluids and minerals lost during treatments. GranuFlo and NaturaLyte are mixed in Fresenius Dissolution Units with ISO 13959 or AAMI RD62 and administered during dialysis treatments for people with severe kidney failure or with end-stage kidney disease.
The products, made and marketed by Fresenius Medical Care North America, have been linked to health complications. Potassium levels have dropped in patients after treatments, causing abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac arrest.
More than 10% of adults in the United States (approximately 20 million people) are living with chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). CKD results when a person’s kidneys stop working properly and can no longer filter waste from the blood. This, in turn, results in additional health problems due to a build-up of toxic-type substances in a person’s body. Without treatment of the condition, CKD can develop into complete kidney failure, requiring regular dialysis.
Dialysis requires the use of a machine to filter blood as a healthy kidney would. Two different types of dialysis include hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
GranuFlo and NaturaLyte are regulated as devices by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. These concentrates make up dialysis solutions used in hemodialysis treatments. The solutions are used in Fresenius’ own clinics as well as other dialysis centers using Fresenius products.
A Class I recall means there is a reasonable probability that use of the product will result in a serious health condition or death of the patient.
The recall was prompted by a high potential for heart attacks, including fatal ones, after dialysis and the company’s alleged failure to alert the public about the risk. Additional recalls, although not as severe, including one for NaturaLyte, subsequently followed.
As of December 2022, these products are still available on the market.
What Is Chronic Kidney Disease?
A person is diagnosed with kidney disease when their kidneys are damaged and they have stopped working properly, meaning they are unable to filter the person’s blood. As waste builds up in a person’s body, risks of other health problems increase as well.
The kidneys are located just below your rib cage and are about the size of your fist. Each person possesses a pair of the bean-shaped organs that are positioned on either side of the spine. The kidneys’ job is to filter a person’s blood by producing urine. The urine is then stored in the bladder and later expelled through the urethra.
The kidneys keep pH levels (acid-base levels) of the body balanced. They prevent the buildup of waste and keep the body regulated with the production of essential hormones and the stabilization of electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium.
The loss of kidney functioning can be either acute (sudden) or chronic (long-term). Acute kidney disease is often temporary and reversible (depending on its cause); whereas chronic kidney disease (CKD) develops over many years and does not have a cure.
Causes, Stages and Complications of Chronic Kidney Disease
Certain conditions can increase a person’s likelihood of developing CKD. The most common causes of CKD include diabetes, high blood pressure, family history of CKD and/or kidney failure, heart disease, obesity (severely overweight), high cholesterol, and lupus (chronic inflammatory disease).
Your risk also increases with age, and men are 50% more likely than women to develop kidney failure.
Potential health effects of CKD may include:
- Retention of excess fluid; swelling in arms and lungs, of fluid in your lungs
- High blood pressure
- Inflammation of membrane around the heart
- High potassium levels in the blood
- Weak and/or brittle bones
- Weakened immune system
- Depression
- Malnourishment
- Increased risk of cardiovascular (heart) disease, heart attacks and stroke
- Premature death
- Low red blood cell count (anemia)
Kidney failure is also called End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). This condition is permanent and results in the complete lack of functioning of a person’s kidneys.
Dialysis Treatment
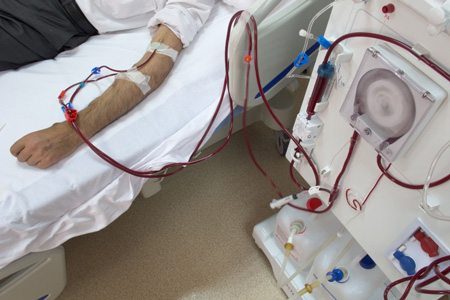
Dialysis is a treatment used for individuals with kidney failure. The treatment is necessary to artificially filter wastes and excess water from a person’s blood. Of the more than 661,000 people living with non-functioning kidneys in the United States, about 468,000 of those individuals are on dialysis, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The remaining individuals are living with a functioning kidney transplant.
Hemodialysis Versus Peritoneal Dialysis
There are two types of dialysis. These include hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of the abdominal cavity to filter the blood. A fluid solution (dialysate) is put into the abdomen and absorbs wastes as they pass through blood vessels in the lining. The wastes are then expelled from the body along with the fluid. This type of dialysis is done every day at home.
Hemodialysis is done about three times a week, most commonly at a dialysis clinic. This type of dialysis extracts blood from the body where it is filtered by what is called a dialyzer (the artificial kidney), and then returned to the body by a separate tube, now rid of wastes and excess water.
The hemodialysis machine has three main jobs:
- To pump blood and regulate blood flow through the dialyzer
- Monitor blood pressure
- Control the rate of fluid removal from the body
What Is Dialysate?
The dialysis solution, or dialysate, assists the hemodialysis machine in controlling a safe rate of fluid removal from the body by restoring some of the necessary water and mineral substances, such as sodium (salt) and potassium, during the treatment process. The solution can be adjusted to accommodate the patient and their body’s specific blood composition.
GranuFlo and NaturaLyte Details
GranuFlo and NaturaLyte are acid concentrates used as one component in mixing the dialysis solution, or dialysate. Other components of the dialysate mixture include water and a base concentrate, such as bicarbonate.
While NaturaLyte is a liquid (acetic acid), GranuFlo is unique in that it is a dry (powder) acid concentrate. GranuFlo is also unique in that it contains a chemical substance called sodium diacetate. That is a combination of both acetic acid (present in NaturaLyte) and sodium acetate. This substance is also commonly found in baked goods and other foods as an agent in killing or stopping the growth of microorganisms.
Dialysate acts as a buffer while also removing wastes, working to correct the electrolyte and acid-base (or pH) imbalance in individuals with kidney failure.
Side Effects, Complications
Patients can experience side effects and other complications associated with the use of GranuFlo and NaturaLyte. Certain potential health effects and complications are also associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and dialysis treatment, in general.
Potential side effects of GranuFlo and NaturaLyte may include:
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- High blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeat (heart palpitations)
- Listlessness
- Low blood pressure
- Lung irritation
- Tearing, eye irritation or serious eye damage if eye contact occurs
- Mild skin irritation
- Muscle cramps
- Vomiting
Chronic overexposure may result in metabolic abnormalities including high levels of sodium in the blood, low levels of potassium in the blood, and excess alkaline levels in the blood or loss of acid in the blood.
Hemodialysis can also result in its own potential side effects and/or complications including infection, poor blood flow or blockages (blood clots), muscle cramps, sudden drop in blood pressure, weakness, dizziness, and upset stomach.
As of December 2022, the last update to the safety information from Fresenius was in 2015. The mixture causes serious eye damage and people handling it must wear eye protection. Chronic overexposure may cause “hypernatremia, hypokalemia,
and alkaosis.”
Heart Complications
Maintaining stability between acid and alkali levels (pH levels) in the body is essential to a person’s overall health. This is a recurrent problem for people with kidney disease because our kidneys are our natural “buffer” system, meaning they function to neutralize acid in our bodies. Too much acid in the body is called metabolic acidosis. If allowed to persist, acidosis results in very low levels of blood pH, which can be fatal.
Acidosis can lead to adverse health complications including the body’s inability to break down certain proteins, malnutrition, defective bone development, drowsiness/fatigue, lack of energy, rapid breathing, shortness of breath, confusion and/or unconsciousness, coma, and death.
Too much alkali in the body’s fluids, or excess base (buffer), can result in alkalosis. This condition has different types. One type is called metabolic alkalosis, which is caused by too much bicarbonate, a form of carbon dioxide, in the blood. This type of alkalosis can be further intensified by certain dialysate solutions used in dialysis treatments, such as GranuFlo and NaturaLyte.
Internal Memo Points to Heart Attacks in Dialysis Patients with Alkalosis
In November 2011, Fresenius Medical Care issued an internal memo linking alkalosis with cardiopulmonary arrest (heart stoppage) in dialysis patients. The memo further stated that “the major cause of metabolic alkalosis in dialysis patients is inappropriately high dialysate total buffer concentration (bicarbonate).” This means that higher concentrations of a base in a dialysate solution are more likely to result in alkalosis in a patient; and studies have found that patients on dialysis suffering from alkalosis are more likely to experience a heart attack or other adverse heart-related event.
In its memo, the company alerted its own doctors working in its company’s dialysis centers about the increased risk of alkalosis occurring in patients using GranuFlo or NaturaLyte in dialysis treatments. It also advised that the improper use of its products seemed to be attributed to a rise in the risk of sudden cardiac arrest in patients. The internal memo wasn’t distributed outside of the company, though, to warn other dialysis centers using Fresenius’ acid concentrates. It was anonymously leaked to the FDA almost five months later.
Dosing Issues
In its 2011 memo, Fresenius explained that the potential for alkalosis and resulting cardiac arrest was likely due to a dosing error. The error did not take into account the breakdown of acetate (a main ingredient present in both GranuFlo and NaturaLyte) by the liver into carbon dioxide in the blood. Patients prescribed GranuFlo or NaturaLyte received an overdose of base concentrate due to the metabolizing of remaining acetate in their blood after dialysis, resulting in alkalosis that, if left untreated, increased the risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
Due to this phenomenon, Fresenius warned physicians that they needed to adjust (lower) the bicarbonate (base) concentrations in dialysate solutions to take into consideration acetate remaining in the blood and unable to be diffused after a dialysis session. This remaining acetate is then converted to serum bicarbonate, essentially increasing a patient’s dose of bicarbonate base.
Fresenius wrote, “The bicarbonate prescription entered into the dialysis machine underestimates the total buffer that the patient receives from the dialysate… since acetate is rapidly converted into bicarbonate by the liver.”
While bicarbonate is essential in preventing acidosis in patients receiving dialysis, too much of the substance can result in alkalosis. Fresenius acknowledged, “Both conditions are associated with poor patient outcomes, including increased mortality risk.”
Low Potassium Linked to Cardiac Deaths
Use of low potassium dialysate has also been associated with heart attacks and sudden cardiac deaths. Chronic overexposure to GranuFlo and NaturaLyte has been linked to low potassium levels in patients.
Severely low potassium levels may result in abnormal heart rhythms (irregular heartbeat), lightheadedness or faintness, and sudden cardiac arrest (heart stops).
Recall History
GranuFlo and NaturaLyte have undergone various recalls ranging from Class I to Class III. Class I recalls means there is a reasonable likelihood that the use of the product will cause serious health problems or even death. A Class III recall is much less severe, meaning that exposure to the product is not likely to cause any health consequence. Recalls generally occur following an influx of adverse reports or upon some adverse scientific finding regarding the product’s safety, or lack thereof.
-
2012
FDA Safety Communication issued in response to a complaint regarding dangers associated with alkali dosing errors in hemodialysis using dialysate concentrates containing acetic acid and acetate, such as GranuFlo and NaturaLyte; the communication included recommendations to health care providers and a reminder that metabolic alkalosis has been associated with a higher risk of death in hemodialysis patients
-
2012
Class I recall – All lots of Fresenius GranuFlo (powder) Acid Concentrate due to risk of alkalosis with acetate containing dialysis acid concentrates; FDA determined the company violated regulations regarding false and misleading labeling
-
2013
Class III recall – Certain lot numbers of Fresenius GranuFlo NaturaLyte Dry Acid Concentrate for Bicarbonate Dialysis due to discoloration; FDA determined the product was “nonconforming”
-
2013
Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) adverse event report received by the FDA for an adverse event occurring in June 2007; the death of a patient by an adverse event relating to the heart after use of the product (NaturaLyte or GranuFlo)
-
2013
MAUDE adverse event report received by the FDA for the death of a patient that occurred in January 2010 following the use of NaturaLyte or GranuFlo; the patient experienced two separate cardiovascular events after using the product, prior to their death
-
2014
Class I recall – Fresenius announced that it was voluntarily recalling 56 lots of NaturaLyte nationwide and in Canada due to bacteria identified in its product that may lead to bacteria in patients’ blood or systemic infection
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch.com representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch.com's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.