Mounjaro vs. Ozempic
Mounjaro and Ozempic are weekly injections approved by the FDA for Type 2 diabetes. Mounjaro is more costly but more effective than Ozempic in controlling blood sugar levels and weight loss but may have additional side effects. People are filing lawsuits related to both Mounjaro and Ozempic due to adverse side effects such as gastroparesis, ileus, and vision loss.
See If You Qualify for a Weight Loss and Diabetes Drug Lawsuit
You may be entitled to compensation if you were injured after taking a medication like Ozempic, Saxenda or Wegovy. For a free case review, complete the form or call 866-898-3173.
- A+BBB Rating
- 4.9 StarGoogle Reviews
- A+BBB Rating
- 4.9 StarGoogle Reviews
- Medically reviewed by Kenneth S. Fill, Pharm.D., MBA
- Last update: June 24, 2025
Differences Between Mounjaro & Ozempic
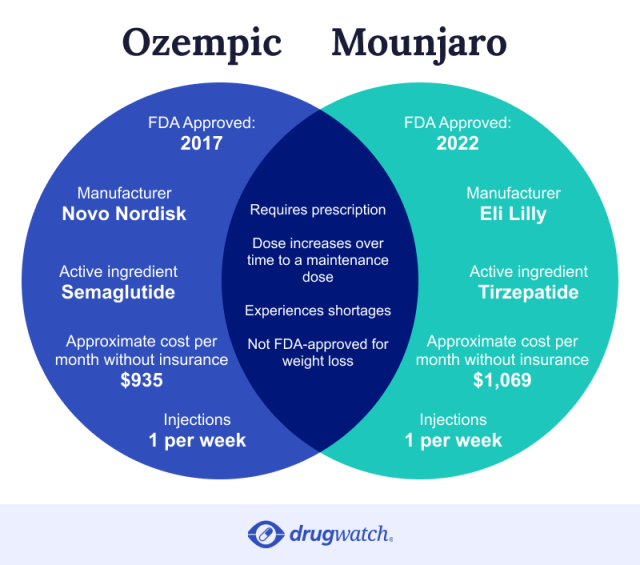
The most significant differences between Ozempic (semaglutide) and Mounjaro (tirzepatide) are their active ingredients and FDA indications. Both are FDA-approved medications for Type 2 diabetes, but Ozempic is also approved to reduce cardiovascular risks and cater to diverse metabolic health needs.
Eli Lilly — which makes Mounjaro — released another tirzepatide medication called Zepbound, which was FDA-approved to treat weight loss in 2023. Likewise, Novo Nordisk — which makes Ozempic — also makes Wegovy, another semaglutide that is FDA-approved for weight loss.
Both Mounjaro and Ozempic may be prescribed off-label for weight loss, but the manufacturers warn against off-label uses.
Ozempic and Mounjaro are each available in different dosages. You inject your dose using a prefilled pen injector once weekly. Each Ozempic pen may contain more than one weekly dose per pen.
| OZEMPIC WEEKLY DOSAGES | MOUNJARO WEEKLY DOSAGES |
|---|---|
| 0.25 mg | 2.5 mg |
| 0.5 mg | 5 mg |
| 1 mg | 7.5 mg |
| 2 mg | 10 mg |
| 12.5 mg | |
| 15 mg |
Health care providers advise against combining Mounjaro and Ozempic because of potential side effects. Both drugs help manage Type 2 diabetes, but taking two GLP-1 medications at the same time is not recommended.
Usage Differences Between Mounjaro and Ozempic
While Mounjaro and Ozempic are both diabetes drugs, they have become popular for weight loss as demand for Wegovy and Zepbound faced shortages. Truveta Research, a coalition of more than 30 health care systems in the U.S., compared Mounjaro and Ozempic based on prescribing and dispensing rates, patient characteristics and other criteria.
| CRITERIA | MOUNJARO | OZEMPIC |
|---|---|---|
| Prescribing Trends | Showed a significant increase in prescribing rates throughout 2023. Increasing trend in first-time prescribing, indicating growing popularity. | Most commonly prescribed GLP-1 receptor agonist. Higher first-time prescribing rates compared to Mounjaro. |
| Dispensing Rates | Lower dispensing rates compared to Ozempic, particularly for anti-obesity medications (AOMs). This may indicate challenges in patient access or acceptance. | Higher initiation rates, with more first-time prescriptions being dispensed within 60 days. More consistent dispensing rates compared to Mounjaro. |
| Patient Characteristics | Showing promising trends, particularly in first-time prescribing rates. Potential for capturing market share, especially among patients seeking weight-loss treatments. | Preferred across different age groups, with consistent prescribing trends observed over time. Higher prevalence in patients with Type 2 diabetes and/or overweight or obesity. |
| Effectiveness & Safety | Emerging as a competitor to established medications like Ozempic. Efficacy and safety profiles may need further evaluation as it gains more usage in clinical practice. | Well-established efficacy in both diabetes management and weight loss. Generally well-tolerated with a good safety profile. |
| Market Access | Shows the potential to challenge Ozempic's market dominance, particularly in the anti-diabetic medication (ADM) category. Access and insurance coverage may influence its adoption rate compared to Ozempic. | The dominant player in the GLP-1 receptor agonist market, with established efficacy and safety data. Higher market share and brand recognition compared to Mounjaro. |
Truveta’s research was based on electronic medical data from health care institutions providing 18% of the daily clinical care in the U.S. The analysis reviewed records of more than one million patients prescribed a GLP-1 between January 2018 and December 2023.
How Do Mounjaro and Ozempic Help Manage Diabetes?
Both drugs help manage Type 2 diabetes. Mounjaro suppresses glucagon, a blood sugar-elevating hormone called GLP-1, and offers comprehensive diabetes management. Ozempic also enhances fullness and lowers blood glucose.
Mounjaro, a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, offers enhanced appetite and blood sugar control mechanisms. This dual action could lead to more weight loss than medications targeting GLP-1. While research shows Mounjaro is more effective for blood sugar control and weight loss, it is more expensive and may have additional side effects.
Mounjaro vs. Ozempic for Weight Loss
While multiple studies show Mounjaro is more effective than Ozempic for weight loss, the FDA has not approved it for that use. But doctors may sometimes prescribe both Mounjaro and Ozempic off-label for weight loss.
Another study by Truveta Research compared Mounjaro’s and Ozempic’s active ingredients in overweight and obese adults. In the real-world comparative effectiveness study, tirzepatide proved more effective for weight loss within a year of treatment.
Tirzepatide users had higher success rates for body weight loss and significant weight loss at three, six and 12 months of treatment.
According to Eli Lilly, participants in Mounjaro clinical trials lost 12 to 25 pounds, with a reported 21.1% weight loss after 12 weeks and a total mean weight loss of 26.6% over 84 weeks.
In clinical trials by Novo Nordisk, Ozempic users lost between 9.3 and 14.1 pounds. On average, they lost about 15% of their body weight after 68 weeks.
Is Mounjaro More Effective Than Ozempic?
The more effective medication depends on your individual needs. While Mounjaro is known for effectively reducing A1C levels and weight, Ozempic also addresses cardiovascular risks associated with Type 2 diabetes.
Several studies have shown that Mounjaro is more effective than Ozempic for blood sugar control and weight loss.
In the SURPASS-2 trial, tirzepatide outperformed semaglutide in reducing A1C levels. Tirzepatide’s 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg doses showed A1C reductions of 2.01, 2.24 and 2.30, respectively, surpassing semaglutide’s 1.86 reduction at the 1 mg dose.
How Do Mounjaro & Ozempic Side Effects Differ?
The drugs have similar side effects, but Mounjaro side effects may be more numerous — and more severe.
“The SURPASS-2 trial, [which] checked head-to-head tirzepatide and semaglutide, results indicated that most common side effects were not significantly different between tirzepatide and semaglutide,” Dr. Eldad Einav, a cardiologist and weight loss specialist, told Drugwatch. “Tirzepatide show[ed] a slightly higher rate of serious adverse events compared to semaglutide.”
Mounjaro’s prescribing information warns of severe gastrointestinal disease, while Ozempic’s does not. In clinical trials, more people stopped taking Mounjaro due to gastrointestinal side effects, and both medications had more side effects at higher doses.
“When comparing the side effects of Ozempic and Mounjaro, it is important to note that each medication affects the body differently, and individual experiences may vary,” Dr. David Smith, urologist and co-founder of medical device company BladGo Medical, told Drugwatch.
| SIDE EFFECT | MOUNJARO | OZEMPIC |
|---|---|---|
| Abdominal Pain | ||
| Constipation | ||
| Decreased Appetite | ||
| Diarrhea | ||
| Dyspepsia (Indigestion) | ||
| Nausea | ||
| Vomiting |
There have also been reports of urinary tract infections, or UTIs, as a rare Ozempic side effect.
“Those who have a history of urinary tract infections may want to avoid Ozempic,” Smith said. “Similarly, individuals who have a history of gastrointestinal issues may want to avoid Mounjaro.”
Smith added that you should talk with your doctor about your medical history to determine which drug may be better for you.
Both drugs have FDA boxed warnings for thyroid gland tumors, including cancer. The drugs also warn about side effects like pancreatitis, diabetic retinopathy, low blood sugar, kidney problems, allergic reactions and sudden gallbladder disease. In cases, the drugs may cause ileus, a digestive problem leading to bowel movement difficulties.
Mounjaro and Ozempic Safety Concerns and Lawsuits
Both patients taking Mounjaro and those taking Ozempic have reported severe gastrointestinal problems leading to hospitalization. Mounjaro’s label advises against using the drug in patients with gastroparesis.
In August 2023, a patient filed both Ozempic and Mounjaro lawsuits after experiencing severe gastroparesis after taking both drugs. The patient experienced chronic, severe vomiting that required hospitalization.
Mounjaro & Ozempic Drug Interactions
Taking Ozempic or Mounjaro may interact with certain medications, leading to an increased risk of hypoglycemia and affecting the effectiveness of oral medications due to changes in stomach emptying.
If you take sulfonylurea or insulin, consult with your doctor about possibly reducing your medication dose while on either drug.
Mounjaro’s drug label recommends using a non-oral contraceptive method or adding a barrier contraceptive for four weeks after starting treatment and for four weeks after each dose escalation.
Cost Differences Between Mounjaro & Ozempic
Mounjaro is more expensive than Ozempic. In early 2024, the cost of Ozempic without insurance started at around $935 a month in the U.S. Mounjaro’s list price was $1,069 per fill, according to the Eli Lilly website. Some reports say the drug can cost as much as $1,267.
Insurance may cover drug costs for diabetes treatment, but weight loss patients face approval challenges. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly offer discount programs for eligible patients.
“I’m very blessed to have insurance pay 100% of my Mounjaro,” Barb Herrera, a health care blogger who takes Mounjaro for Type 2 diabetes, told Drugwatch. “I am grateful and hope my insurance continues to pay for it.”
She said she knows several people without insurance who rely on compounding pharmacies to buy versions of semaglutide or tirzepatide.
Should You Take Mounjaro or Ozempic?
Choosing between Mounjaro and Ozempic depends on your specific medical requirements.
For instance, the FDA approved Ozempic in March 2024 to prevent heart complications in overweight and obese adults.
“People with preexisting coronary disease will benefit from semaglutide based on the SELECT trial showing 20% less heart attack and stroke in patients taking Wegovy for weight loss,” Dr. Einav said. “Tirzepatide does not [yet] have this data.”
Ozempic lowers A1C levels, aids in weight loss and reduces the risk of cardiovascular events in people with established cardiovascular diseases.
Mounjaro is more effective for weight loss and reducing A1C levels, but it may cause severe gastrointestinal side effects. Before deciding, consult your health care provider to discuss the benefits and drawbacks of each medication.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch.com representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch.com's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.

