Cymbalta
Cymbalta is an antidepressant approved to treat mood and pain disorders. It was one of Eli Lilly’s most profitable drugs. It works by preventing the body from reabsorbing two neurotransmitters: serotonin and norepinephrine. The drug has a long list of interactions, and possible side effects include nausea, increased sweating and withdrawal symptoms.
- Medically reviewed by Kenneth S. Fill, Pharm.D., MBA
- Last update: March 10, 2025
Cymbalta comes in delayed-release capsules and is part of a drug class called serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, or SNRIs. Eli Lilly and Company manufactures the medication. Duloxetine is the drug’s active ingredient.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration first approved the antidepressant in 2004. The drug quickly grew in popularity. In 2009 alone, doctors wrote 14.6 million prescriptions, according to The New York Times.
At its peak in 2012, the drug had annual sales of $4.99 billion, according to Indy Star. The drug’s patent ran out in 2013, opening the door to several generic manufacturers.
A Sept. 30, 2018, quarterly filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission reported Cymbalta had brought in $523.5 million worldwide in nine months for the drug maker in 2018, including $39.3 million in the United States.
Depending on the dose strength, the medication can cost anywhere between $242.73 and $472.66 for a 30-day supply, according to Drugs.com. One 2022 research report noted that, for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, costs of duloxetine varied from $12 (generic) to $529 (brand name).
Uses, Dosages and Strengths
The FDA originally approved Cymbalta for major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. The agency has since approved the medication for diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia and chronic musculoskeletal pain in adults. The drug is not approved for use in children and teens.
Eli Lilly had tried to get the drug approved for stress urinary incontinence as well. But the FDA suggested it could not grant approval based on the data the company had provided, so the drug maker withdrew its application in 2005, according to a company press release.
Then, the company began investigating duloxetine to treat children with fibromyalgia. It updated its Phase III clinical trial progress on Aug. 14, 2018, on ClinicalTrials.gov. Eli Lilly researcher Dr. Himanshu P. Upadhyaya and colleagues presented the study results at the 2018 World Congress on Pain in Boston. They concluded duloxetine may not be effective in treating juvenile primary fibromyalgia syndrome compared to a placebo.
Depending on the treatment indication and the patient’s age, doctors may prescribe different strengths. The medication comes in 20 mg, 30 mg and 60 mg delayed-release capsules.



- Major Depressive Disorder
- 40 mg to 60 mg a day. The maximum dose is 120 mg a day.
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- 60 mg a day. The maximum dose is 120 mg a day.
- Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
- 60 mg a day. The maximum dose is 60 mg a day.
- Fibromyalgia
- 30 mg a day. The maximum dose is 60 mg a day.
- Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
- 30 mg a day. The maximum dose is 60mg a day.
Patients should swallow capsules whole with or without food. If patients miss a dose, they should take the missed dose as soon as possible, but they should not take two doses at the same time.
Major Depressive Disorder
The FDA first approved Cymbalta to treat major depressive disorder (MDD) on Aug. 4, 2004. MDD is also called clinical depression or just simply depression. It is a persistent feeling of sadness and a loss of interest. MDD is a common but serious mood disorder and can cause severe symptoms that can affect how a person thinks or feels. It can also interfere with a person’s daily routine, disrupting how a person eats, sleeps or works.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
In February 2007, the FDA approved Cymbalta for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). In November 2009, the FDA approved Cymbalta for the maintenance of GAD. The FDA approved Cymbalta to treat GAD in children and adolescents in 2014. However, doctors must carefully weigh the risks and benefits of prescribing Cymbalta to children, teens and young adults. Cymbalta’s label carries a black box warning — the most serious kind from the FDA — warning that use of the drug may lead to an “increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents and young adults taking antidepressants.”
Generalized anxiety disorder is the constant state of worry about everyday problems — health, finances, relationships and employment — well beyond their proportions for at least six months. It can worsen if the patient faces additional stress or if it persists over time.
GAD affects more than 3% of the U.S. adult population and can be serious in almost a third of the people who have it. Fewer than half of the people who suffer from generalized anxiety disorder receive treatment.
Fibromyalgia
In June 2008, the FDA approved Cymbalta for the management of fibromyalgia — a chronic, widespread pain disorder.
Fibromyalgia is characterized by pain and tenderness throughout the body in a way that reduces a person’s ability to function or affects their overall quality of life. Between 1% and 5 % of U.S. adults have fibromyalgia, with women being far more likely than men to develop it. As much as 90% of people with fibromyalgia are women. Most cases develop in people between the ages of 40 and 70.
Duloxetine, the active ingredient in Cymbalta, is one of three drugs approved by the FDA to treat fibromyalgia. The other two are pregabalin (Lyrica) and milnacipran (Savella).
Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
In November 2010, the FDA approved Cymbalta for the treatment of musculoskeletal pain. Musculoskeletal refers to the combined workings of the body’s skeleton and muscles.
Musculoskeletal pain is one of the most common types of pain, with about 75% of Americans experiencing it at some point in their lifetime. Osteoarthritis and lower back pain account for the majority of chronic cases, defined as pain that lasts longer than three months, typically outlasting a normal healing process for an injury.
In approving Cymbalta for chronic musculoskeletal pain, the FDA acknowledged Cymbalta’s link to serious side effects including suicide, suicidal thoughts and behavior, liver damage and pneumonia. But the agency said there were few other drugs as effective in treating musculoskeletal pain.
“While these serious side effects have been associated with the use of Cymbalta, they have occurred in less than 1% of treated patients,” the FDA said in a statement. “There are a finite number of drugs available for the treatment of chronic musculoskeletal pain, all of which are associated with rare, serious side effects. There are patients in whom none of the available treatments are effective.”
How Duloxetine Works
Researchers believe duloxetine works by increasing the activity of serotonin and norepinephrine in the central nervous system, according to the drug’s label.
The National Institutes of Health says duloxetine increases the levels of the neurotransmitters in the brain by preventing the body from reabsorbing them, and this contributes to its antidepressant effects.
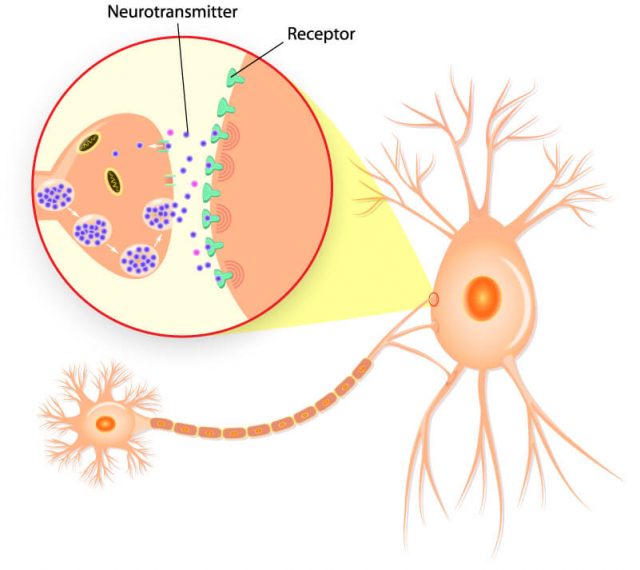
Depression, chronic pain and anxiety have inter-related symptoms, according to researcher Cheryl L. Wright and fellow researchers at the Oregon Health and Science University School of Nursing. Researchers believe duloxetine treats general pain disorder, diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in the same way it treats depression and anxiety.
Researchers know the drug does not repair the nerve damage that leads to diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but clinical trials have shown the drug can relieve the pain and other sensations associated with the condition, according to an Eli Lilly statement.
“While additional non-industry-sponsored investigation is warranted, the evidence to date suggests that in those with [fibromyalgia], duloxetine has largely been a safe and, in some, a promising intervention to manage chronic pain.”
Adjusting the levels of neurotransmitters can also relieve fibromyalgia pain without affecting mood, Wright and colleagues wrote in Expert Review of Clinical Immunology.
“While additional nonindustry-sponsored investigation is warranted, the evidence to date suggests that in those with [fibromyalgia], duloxetine has largely been a safe and, in some, a promising intervention to manage chronic pain,” the researchers wrote. “As with the introduction of any new pharmacologic agent, each patient deserves close monitoring to assess the drug’s effectiveness as well as adverse effects.”
Side Effects
Five percent or more of the people who had taken Cymbalta during clinical trials reported common side effects at least twice as often as those who had taken a placebo. According to the drug’s label, the most common side effects of Cymbalta were nausea, dry mouth, sleepiness, constipation, loss of appetite and increased sweating.
Though rare, serious side effects can include life-threatening conditions, and the FDA has released several warnings for side effects such as liver disease and low blood pressure. The medication carries a black box warning for suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children, adolescents and young adults.
Patients should talk to their doctor as soon as they notice any changes in their condition. Many side effects will simply work themselves out in time, but a doctor may need to adjust the medication dosage.
Never stop taking duloxetine suddenly or without first consulting a doctor, even if you experience side effects. Stopping the medication abruptly can trigger withdrawal symptoms, including dizziness, headache, nausea, diarrhea, tingling sensation, irritability, vomiting, insomnia, anxiety, increased sweating and fatigue.
The medication insert recommends doctors gradually reduce the dose rather than suddenly stopping treatment. Some people who say they suffered withdrawal side effects filed lawsuits against Eli Lilly.
Food, Alcohol and Drug Interactions
Medications that may interact with Cymbalta range from over-the-counter pain relievers to prescription blood pressure medicines, according to Everyday Health. The drug’s label has a long list of possible interactions.
Taking duloxetine with certain other drugs can affect serotonin levels, blood pressure and body temperature. It can lead to a life-threatening condition called serotonin syndrome.
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome can include agitation, confusion, diarrhea and dilated pupils. Other signs to look for are elevated blood pressure, heavy sweating and rapid heart rate. The condition can also cause muscles to be rigid or twitch.
Mixing Cymbalta with grapefruit or grapefruit juice may increase the risk of side effects or overdose. The acidic fruit interferes with the metabolism of the drug and may allow it to build up in the patient.
Light drinking of alcohol does not appear to enhance duloxetine’s effects. But heavy alcohol drinking can contribute to liver stress or damage.
Drugs and substances that may interact with Cymbalta include:
- MAO Inhibitors (Nardil, Parnate, others)
- SSRIs (Celexa, Fluvoxamine, Lexapro, Prozac, Paxil, Symbyax, Zoloft)
- Triptans (Amerge, Axert, Frova, Imitrex, Masalt, Replax, Zomig)
- Other SNRIs (Pristiq, Fetzima, Ixel, Savella, Elamol, Tofacine, Effexor)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (Anafranil, Ascendin, Norpramin, Sinequan)
- Aminoketones (Wellbutrin)
- Fluoroquinolone antibiotics (Cipro, Levaquin, Avelox)
- St. John’s Wort
- NSAIDs such as ibuprofen
- Aspirin
- Warfarin
- Drugs that affect gastric acidity
- Caffeine
This is not a complete list of all food and drug interactions. Patients should talk with their doctors about any drugs or supplements they are taking as well as alcohol use and diet to make sure they are not exposed to a potential interaction.
Before You Take Cymbalta
Some complications can be prevented if patients have an honest discussion with their doctors before starting treatment. This will also ensure patients receive the most effective treatment the drug can deliver.
- The most bothersome symptoms
- Thoughts of harming themselves
- Previous medicines taken for their condition
- How effective other medicines were or if they caused any side effects
- Other mental or physical health conditions including bipolar disorder, kidney or liver disease
- Other medications the patient is taking including over-the-counter drugs and supplements
- Allergies to any medications
- Other mental health treatment such as talk or substance therapy
- Current or planned pregnancy or breastfeeding
- Alcohol or drug use
Misleading Ads
The FDA has repeatedly reprimanded Eli Lilly for running misleading ads that overstate the benefits of Cymbalta while downplaying the risks.
In 2005, the FDA said Eli Lilly had run ads in a medical journal that were misleading because they failed to disclose important risks and side effects, Pharma Times reported.
Then, in 2007, the FDA called out the company for using a professional mailer that “overstates the efficacy of Cymbalta and omits some of the most serious and important risk information associated with its use.”
Eli Lilly suggested patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy “experienced significantly less pain interference with overall functioning” but there was no evidence the claim was true, the FDA said in a letter to the company.
In an ad in the WebMD Little Blue Book of Rheumatology, the drug maker claimed patients with fibromyalgia could achieve a 30% improvement in pain after taking Cymbalta, MedCity News reported. The FDA said in 2010 that no data existed to support the claim.
In all these cases, the FDA ordered Eli Lilly to stop the ad campaigns.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch.com representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch.com's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.


