Talcum Powder & Ovarian Cancer
Due to the rarity of ovarian cancer, studying its connection with talcum powder is challenging. While research is inconclusive, a study by the American Cancer Society lists talcum powder as a risk factor for ovarian cancer, the deadliest cancer of the female reproductive system.
Can Talcum Powder Cause Ovarian Cancer?
To date, there is no definitive evidence to show how talcum powder causes ovarian cancer. But as early as 1971, researchers reported finding talc “deeply embedded” in cervical and ovarian cancer tumors.
Studies suggest a potential link between talc use and ovarian cancer, but there’s no conclusive evidence, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. To ensure consumer safety, the FDA conducts ongoing testing for asbestos contamination in talc-based cosmetics.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer previously classified talc-based body powder as possibly carcinogenic to humans in the female genital area. In July 2024, the agency re-classified talc from a “possible carcinogen” to a “probable carcinogen.” This is the second highest level for certainty that a substance causes cancer, and the researchers reached their decision in part from limited evidence that talc increases risk of ovarian cancer in humans.
Talcum powder is made from talc, a mineral that reduces friction and absorbs moisture and odor. It is often found close to asbestos, a mineral known to cause cancers — notably mesothelioma.
According to the American Cancer Society, talcum powder containing asbestos is classified as carcinogenic, but the classification for asbestos-free talc is uncertain.
One hypothesis researchers have studied is the possibility that talc particles from feminine hygiene talcum powder may travel to the ovaries through the reproductive system, leading to long-term inflammation and increased cancer risk.
Tens of Thousands of Lawsuits Claim Talc Caused Ovarian Cancer
Thousands of ovarian cancer patients and their families have sued Johnson & Johnson, claiming it failed to adequately warn consumers of studies linking its products to ovarian cancer. The company does not include an ovarian cancer warning on its products despite research that shows the potential increased risk of ovarian cancer.
As of July 2024, Johnson & Johnson faced 57,624 talcum powder lawsuits in a federal multidistrict litigation.
In May 2024, the company offered $6.48 billion to settle all ovarian cancer lawsuits against the company. By 2020, Johnson & Johnson discontinued using talc in its powder products sold in the U.S. It discontinued talc globally in 2023. In both cases, the company replaced talc with cornstarch.
“Johnson & Johnson’s move to discontinue its iconic talc-based baby powder could be viewed as a prudent business decision to limit further legal exposure, even as the company maintains the products are safe,” Lyle Solomon, principal attorney at Oak View Law Group in Auburn, California, told Drugwatch.
The company said the decision is purely financial and that its talc powders do not cause cancer and don’t contain asbestos.
Over 40 Years of Talc Ovarian Cancer Studies
Research going back to the 1960s has shown associations between talc and ovarian cancer.
In 1971, scientists in Wales pointed to a possible connection between the dusting of female genitals with talcum powder and ovarian cancer. They discovered particles of talc embedded in ovarian and cervical tumors.
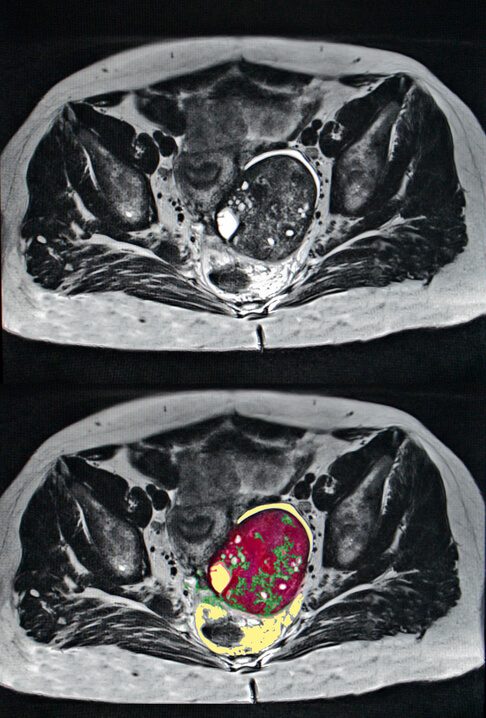
However, recent research has been inconsistent as to the relationship between talcum powder and ovarian cancer.
- Long-Term Talc Use
- A 2024 study published in Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy suggested long-term talcum powder use in the genital area may increase ovarian cancer risk. It found talc can induce molecular changes associated with cancer development by causing oxidative stress, gene mutations and inflammatory responses. Researchers said talc can induce molecular changes associated with cancer development.
- Mixed Results
- The National Cancer Institute reported in 2024 that case-controlled and cohort studies regarding talc links to ovarian cancer were inconsistent. Many cohort studies, including a cohort study among nurses, did not find any association between perineal talc use and the development of ovarian cancer.
- Recall Bias May Play a Role in Research
- A 2024 Global Epidemiology study looked at the effect of recall bias in talc studies. While case-control studies suggest a slight increase in risk, cohort studies consistently find no association. Quantitative analysis reveals recall bias — where study outcomes can affect individuals' memory and perception of risk factors — significantly influences the reported risk.
Study: Talc Industry Influence Over FDA
Because talcum powder is considered cosmetic, it has been largely self-regulated by the industry that mines, refines and sells it rather than by the FDA.
A 2021 research article published in New Solutions found extensive influence exerted by the talc industry over the FDA, particularly regarding regulating cosmetic talc products. The researchers reviewed corporate documents uncovered in talc lawsuits and government documents obtained through FOIA requests.
Despite evidence of asbestos in talc dating back to the 1960s, the study found industry pressure delayed and blocked federal regulation, allowing the continued sale of potentially harmful products.
The study’s authors said the industry manipulated testing methods, suppressed evidence and influenced regulatory proceedings to maintain profits. Even after citizen petitions and legal actions, the FDA relied on industry-provided information and rejected calls for regulation.
According to the study, the industry’s influence extended beyond the FDA, impacting other regulatory agencies and standards-setting organizations.
Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that affects the ovaries. It happens when cells in the ovaries start to grow and multiply quickly, which can harm the healthy tissues in the surrounding area.
The ovaries produce eggs and female hormones. Ovarian cancer is uncommon but causes more deaths than any other female reproductive cancer. Early detection and treatment improve the chances of recovery. Unfortunately, symptoms may be mild or absent until they progress to an advanced stage.
- Abnormal periods
- Back pain that gets worse
- Bloating
- Gas, nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite, feeling full too quickly or difficulty eating
- More frequent or urgent need to urinate and/or constipation
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Pain or pressure in the pelvic area
- Vaginal bleeding or abnormal discharge
- Weight gain or loss
Diagnosing ovarian cancer typically involves a physical exam, a pelvic exam, lab tests, an ultrasound or a biopsy. To treat ovarian cancer, doctors usually recommend a combination of surgery and chemotherapy.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch.com representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch.com's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.






