Birth Control
Most Americans use birth control to prevent pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases. There are many types of birth control available in the U.S. Each varies in cost, effectiveness and side effects. Some have even led to injury lawsuits.
Birth control allows people to stop pregnancy before it begins. It is also called contraception. About 99 percent of American women ages 15 to 44 who have ever had sexual intercourse have used contraceptives.
Some birth control methods are more effective than others. Their cost varies, too. Abstinence is the only method that is 100 percent effective and free.
Not all types of birth control protect people from sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs. Only latex condoms and abstinence protect people from STDs.
Most types of birth control are relatively safe for women’s health and men’s health. But some may have serious side effects.
Certain birth control side effects led women to file personal injury lawsuits.
Types of Birth Control
There are several types of birth control. These range from birth control pills to sterilization by tubal ligation or vasectomy. Most types of birth control are for women, but there are also options for men.
Each type of contraception has its own side effects, benefits and effectiveness.
- Hormonal (birth control pills, NuvaRing, patches and shots)
- Barrier methods (condoms)
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs) (copper and hormonal)
- Surgical (tubal ligation, vasectomy)
- Implants (Essure, Norplant, Nexplanon)
- Emergency contraception (Plan B)
Depending on the type of contraception you’re considering, you may have options to order birth control online. Consult a doctor before making a decision about your health care.
Types of Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal birth control is the most popular type of birth control in the U.S. These methods include the pill, the patch, a shot and NuvaRing.
They work by releasing estrogen, progestin or a combination of both. These hormones stop the woman’s body from releasing an egg.
They may also thicken cervical mucus. Thick mucus makes it difficult for the sperm to reach the egg.
Research is underway to develop a hormonal birth control pill for men. The experimental drugs are part of a class of drugs known as progestogenic androgens, and they work by lowering testosterone levels.
Birth Control Shot
The birth control shot (Depo-Provera & Depo-SubQ Provera) is a progestin injection. A doctor or a nurse administers the birth control shot.
Women using this method get a birth control shot every three months. It causes an increased risk of bone thinning.
- Effectiveness: 94 percent
- Side Effects: Headaches, changes in appetite, weight gain, increased spotting, irregular periods (first six to 12 months), nausea, changes in sex drive, bone thinning, depression
- Average Cost: $0 to $100
Yaz Birth Control and Other Birth Control Pills
Several brands of birth control pills are available to women in the U.S. Women must take the pill every day to prevent pregnancy.
Most side effects of birth control pills are mild and go away after two or three months.
But some brands might have more side effects than others. For example, all combination birth control pills, including Yaz, have a warning for an increased risk for blood clots and strokes, especially in women who smoke cigarettes and are over the age of 35. Yaz and other birth control pills that contain the hormone drospirenone may have a greater risk for these side effects than other birth control pills.
Older oral contraceptives “appear to be a safer choice with regard to venous thromboembolism (blood clots) than preparations containing drospirenone,” Dr. Susan Jick of Boston University’s School of Medicine said in a study in British Medical Journal.
There have been thousands of Yaz lawsuits. Women accuse the pill’s maker, Bayer, of intentionally hiding the drug’s risks.

- Effectiveness: 91 percent effective
- Side Effects: Headaches, changes in sexual desire, bloating, changes in mood, weight changes, irregular bleeding, breast tenderness, blood clots
- Average Cost: $0 to $50
NuvaRing Birth Control
NuvaRing is a flexible ring that contains estrogen and progestin hormones. Women insert a new ring into their vaginas every month.
They may choose to wear it all month and not get a period. Or women can remove NuvaRing in the fourth week to get a period.
Minor NuvaRing side effects go away in a few months. Serious side effects can have lasting effects. Nuvaring increases the risk of heart attack, stroke and blood clots, especially in women over 35 who smoke.

- Effectiveness: 91 percent
- Side Effects: Irregular period, depression, headache, changes in weight, breast tenderness, increased body hair, loss of scalp hair, increased vaginal wetness
- Average Cost: $0 to $200
Birth Control Patch
The birth control patch contains estrogen and progestin. Women may wear it on their buttocks, upper arm or lower abdomen. The birth control patch gets changed every three weeks.
Women over 35 who smoke may have an increased risk of blood clots or heart problems with use of the patch.

- Effectiveness: 91 percent
- Side Effects: Headaches, changes in sexual desire, bloating, changes in mood, weight gain, irregular bleeding, breast tenderness, blood clots, skin irritation
- Average Cost: $0 to $150
Barrier Method: Condoms
After the pill, condoms are the most popular type of reversible birth control. Condoms are small pouches made of latex, plastic or lambskin.
Men wear condoms over the penis. Female condoms (FC2 Female Condom) go inside the vagina. Both types prevent sperm from entering the vagina.
Generally, condoms don’t have many side effects. But, some manufacturers cover condoms in talcum powder.
Some studies show genital exposure to talcum powder may increase the risk of ovarian cancer.

- Effectiveness: 79 percent to 85 percent
- Side Effects: Skin irritation (from lubricants, spermicides or latex) and possible ovarian cancer (from talcum powder)
- Cost: $0 to $2

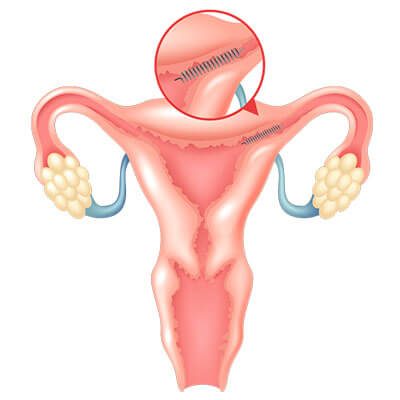
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Mirena and Paragard
Intrauterine devices or IUDs are small, T-shaped plastic devices inserted into the uterus. The FDA approved five IUD brands for sale in the U.S.: Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, Skyla and Paragard.
Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta and Skyla
Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta and Skyla use progestin hormones to prevent pregnancy. They stop egg production in the ovaries.
The most popular IUD on the market is Mirena (levonorgestrel). It is very effective at preventing pregnancy. But, women have reported serious side effects from using Mirena.
It is also linked to a rare disorder called intracranial hypertension. This is also called pseudotumor cerebri. The condition mimics the effects of a brain tumor.
Paragard
Unlike Mirena birth control and other IUDs, Paragard doesn’t contain hormones. It uses copper to prevent pregnancy for up to 12 years. The copper prevents sperm from getting to the egg.
Paragard also works well for emergency contraception. Health care providers must insert it within five days of unprotected sex for it to work.

- Effectiveness: 99 percent
- Side Effects: Infections, device migration, device expulsion, ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterus), organ perforation, cramping, irregular periods, heavy bleeding (ParaGuard), pain during sex, removal may require surgery, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Cost: $0 to $1,300

Permanent Birth Control Surgery: Tubal Ligation and Vasectomy
Tubal ligation (tying the tubes) and vasectomy are two main birth control surgeries. Both procedures are permanent.
Tubal ligation permanently closes or blocks the fallopian tubes. Vasectomy cuts or blocks the tubes that carry sperm.
Generally, vasectomy costs less and has fewer complications than tubal ligation.
- Effectiveness: 99 percent
- Side Effects: Surgical complications, ectopic pregnancy, infections
- Cost: $0 to $1,000 (vasectomy), $0 to $6,000 (tubal ligation)
Birth Control Implants: Essure, Nexplanon
Birth control implants can be permanent or temporary. For example Essure is a permanent birth control implant. It is a non-surgical form of female sterilization.
Doctors insert a metal coil with plastic fibers in each fallopian tube. After three weeks, scar tissue blocks each tube.
The Essure procedure “took a long time, and it was painful,” Angie Firmalino, who underwent the procedure in 2009, told Drugwatch.
Thousands of women say they experienced serious side effects from Essure birth control. Reported injuries range from severe pelvic pain to autoimmune disorders. There are about 35,000 women in one support group called Essure Problems.
Nexplanon is a matchstick-size hormonal birth control implant that goes into the upper arm. It releases a progestin hormone and prevents pregnancy for up to four years.
An older, similar birth control implant called Norplant is no longer available in the U.S. Women filed lawsuits claiming the company did not warn them of serious side effects.
One woman told Drugwatch she developed a tumor from Norplant.
- Effectiveness: 99 percent
- Essure Side Effects: Pelvic pain, autoimmune disorders, dizziness, cramping, vomiting, device expulsion, device migration, abnormal bleeding, painful intercourse, headaches, body pain, additional surgeries for removal, hysterectomy.
- Nexplanon Side Effects: Changes in period, weight gain, liver disease, weight gain, depression, increased blood sugar, gallbladder disease, ovarian cysts, acne.
- Cost: $0 to $2,500
Emergency Contraception: Plan B
Emergency contraception can prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex. These contraceptives are also called “morning after pills.”
The most popular brand is Plan B. Other brands are Take Action, Next Choice One-Dose and My Way.
Emergency contraception is available without a prescription. This is unlike most other types of birth control.
Women have to take emergency contraception within five days of unprotected sex for it to work. It works best within three days.
Paragard copper IUDs also work as emergency contraception.
- Effectiveness: 75 percent to 89 percent
- Side Effects: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness, menstrual pain, breast tenderness, headache, fatigue, irregular bleeding
- Cost: $0 to $60
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch.com representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch.com's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.



